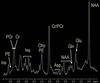
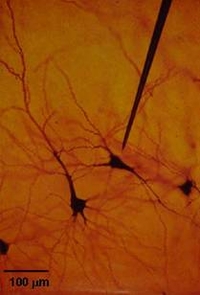
Electrophysiology
The neurons of the brain communicate with each other through electrical signals that can be measured with the appropriate probes. In order to measure the signal of a single cell or of a very small number of cells, microelectrodes as thin as a hair are placed in the cortex of the brain.
Electrophysiology is one of the classic methods of brain research. It is one of the most sensitive and most accurate methods of all, and it is employed routinely in medicine during brain surgery. Although the patients are awake and conscious, they do not feel anything during the measurements, for the brain itself does not feel pain.
Electrophysiology is one of the classic methods of brain research. It is one of the most sensitive and most accurate methods of all, and it is employed routinely in medicine during brain surgery. Although the patients are awake and conscious, they do not feel anything during the measurements, for the brain itself does not feel pain.