Histology
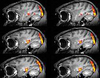
The goal of neuroanatomy is to decipher the organization of the brain.
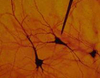
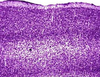
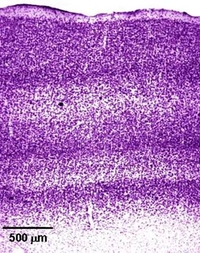
Histology – the science of biological tissues – plays a major role. With the aid of precision instruments, thin sections of brain tissue are prepared which are only a few thousandths of a millimeter thick. A variety of staining techniques can then be used to visualize specific cells or cell structures. The stained sections are then viewed under the microscope, analyzed and documented.
Histology – the science of biological tissues – plays a major role. With the aid of precision instruments, thin sections of brain tissue are prepared which are only a few thousandths of a millimeter thick. A variety of staining techniques can then be used to visualize specific cells or cell structures. The stained sections are then viewed under the microscope, analyzed and documented.